History of the SLUB
On the Emergence and Merging of Two Traditional Libraries
Since 2002
- 1999: The construction of a new central building on the TU Dresden campus began.
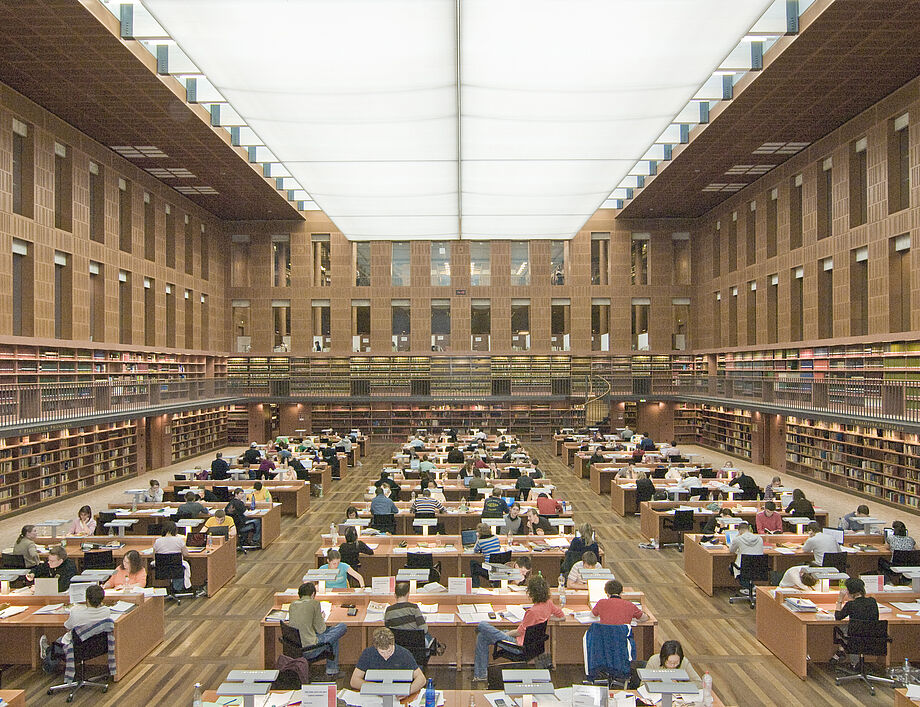
- 1 August 2002: Opening of the central building for users. The decentralised Dre.Punct location becomes the divisional library for the STEM subjects. The decentralised branch libraries for Law, Education, Medicine and Forestry remain in their places.
- Today, the SLUB is one of the largest and most efficient academic libraries; it sees itself as an innovation and coordination centre from the paper library to the digital library.
1996 - 2002
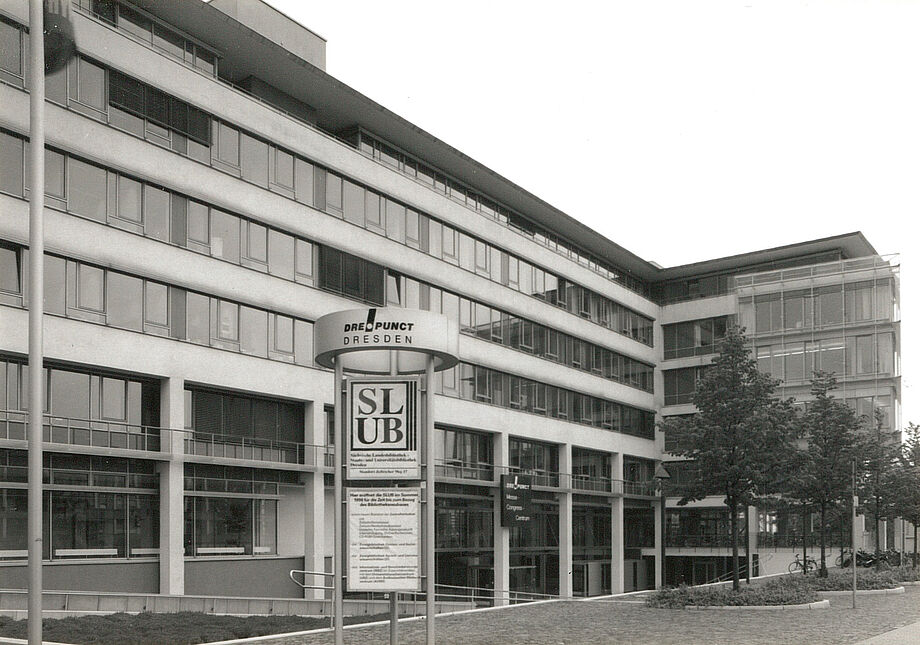
- Since August 1996, the office building "DrePunct" has been the seat of the general management and the administration of the Saxon State Library - Dresden State and University Library, in which the State and University Library merged.
- From summer 1998, the holdings of some branch libraries are also housed here
- To this day, the DrePunct, as a departmental library, is the SLUB's largest location after the Central Library.
Dresden University Library
1945 - 1996
- 1945: Relocation of the then library of the TH Dresden (with 55,000 saved volumes) to the former fraternity house of the "Erato" singers' society.
- 1957: Opening of two reading rooms.
- Since 1961, the former TH has been operating under the name of Technical University.
- 1968: Merger of the 121 decentralised sectional libraries into 26 sectional and other libraries
- 1983/84: Designation as the Central Technical Library of the GDR/Central Specialist Library of the GDR for Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
1875 - 1945
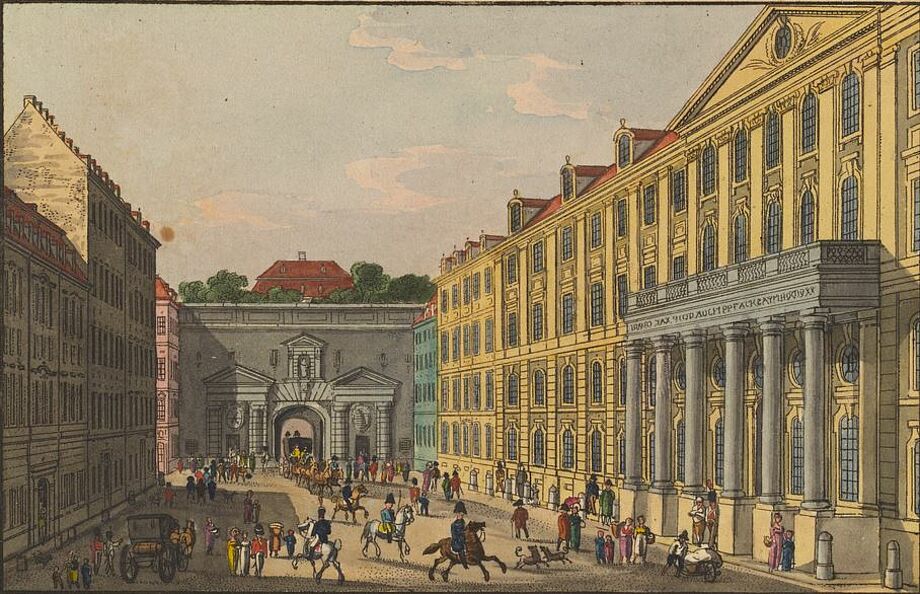
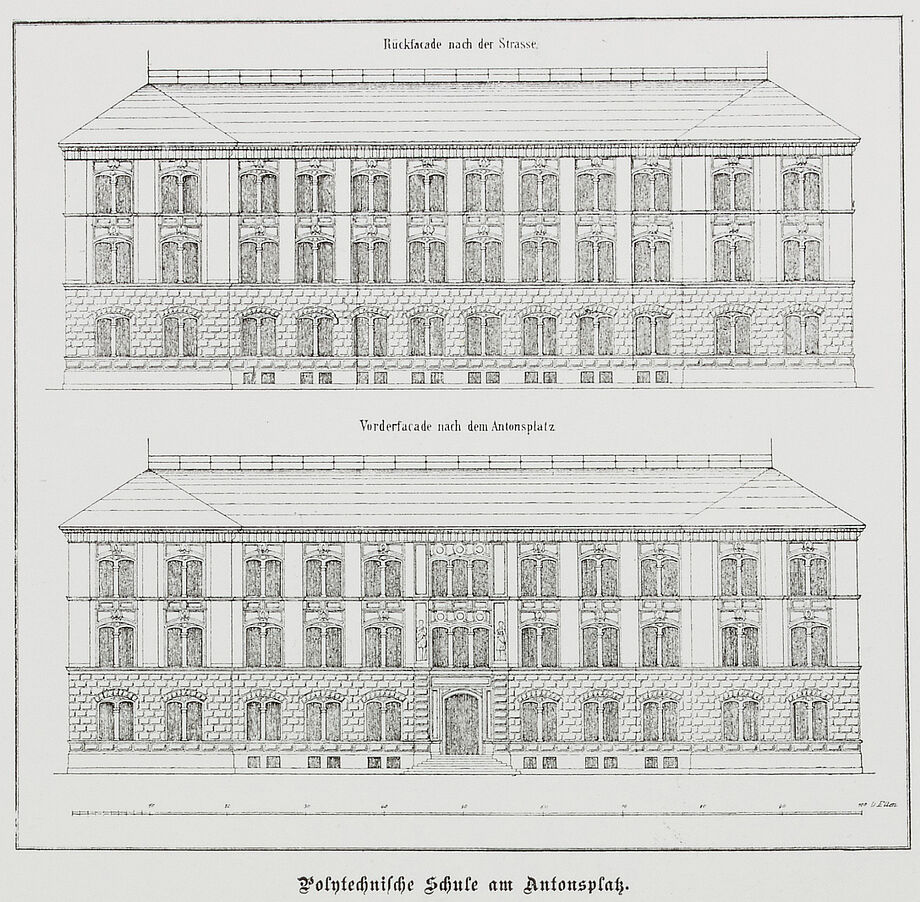
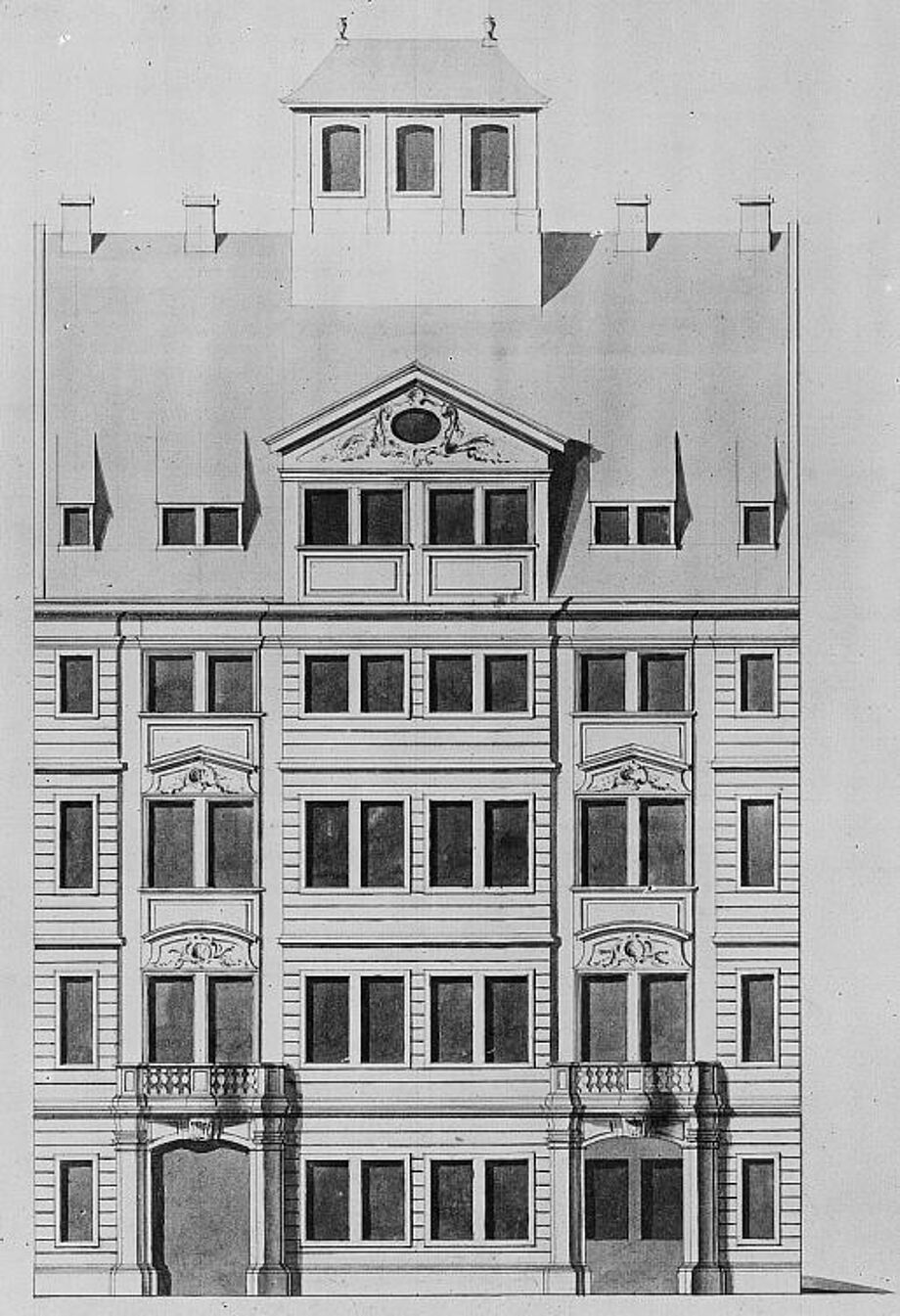
- 1875: The Polytechnic (from 1890: Technical University) and the library move to a new building south of the main railway station, a reading room is available for the first time.
- At the end of the Second World War, the university library loses its domicile, a considerable part of its holdings and a large number of important catalogues
1828 - 1832
- Initially, the libraries of the Landes-Ökonomie-Manufactur, the Commerzien-Deputation and the Ökonomische Gesellschaft are used on loan to supply literature to the Königlich-Sächsische Technische Bildungsanstalt (Royal Saxon Technical College)
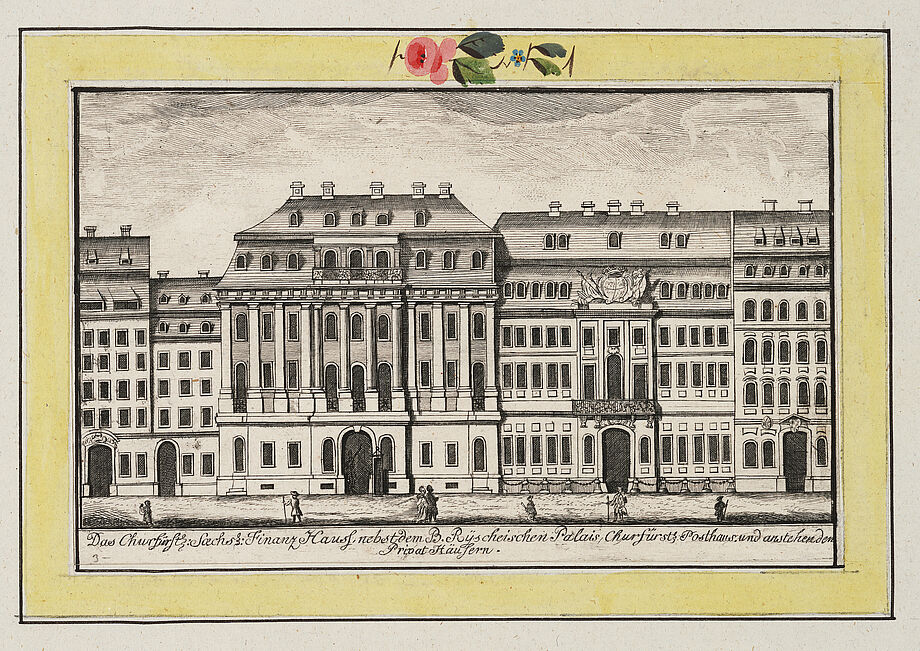
- The library finds its first domicile in the Finanzhaus
Regional Library
1947 - 2002
- Since 1917, operating as the (Royal) Saxon State Library, developing into one of the most modern academic libraries in Germany.
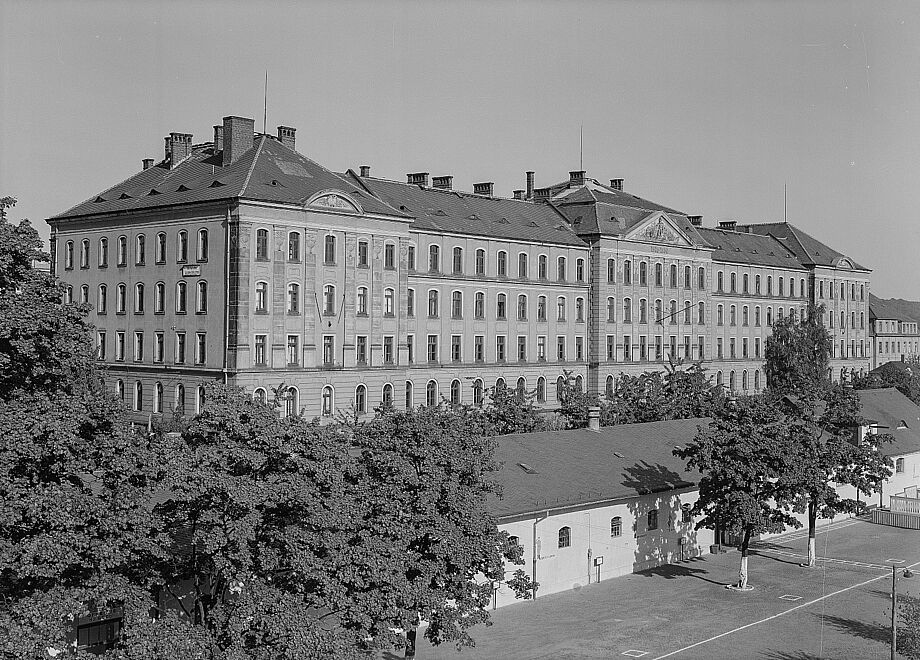
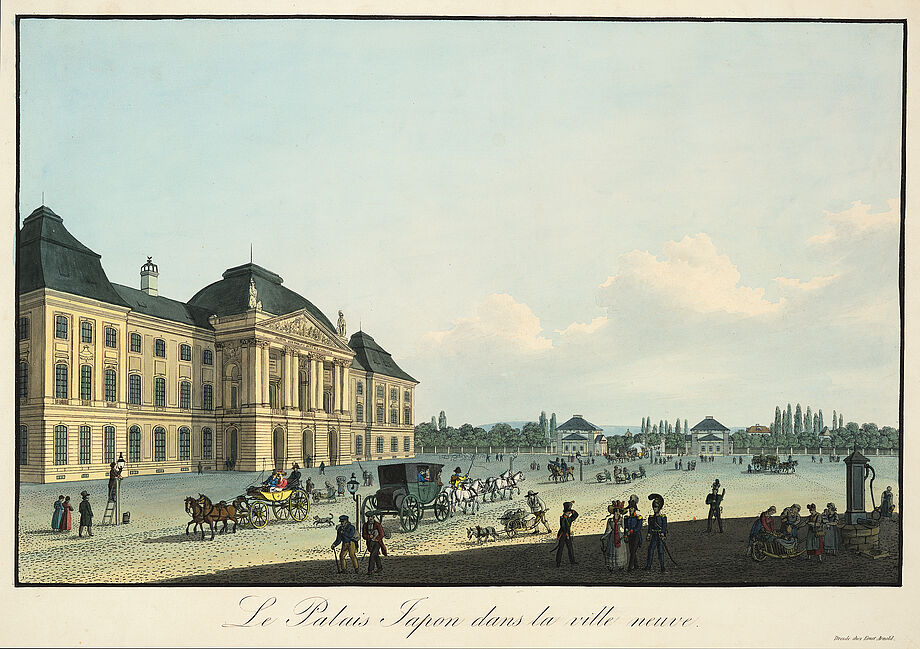
- After the destruction of the Japanese Palace in the Second World War, the library moves to the barracks in Marienallee
- The SLB is the only one of the state libraries in the GDR to retain this function
- 1983: Establishment of the collection focus on fine arts and music
- Integration of the previously independent Deutsche Fotothek (German Photo Library) as a department
1574 - 1586
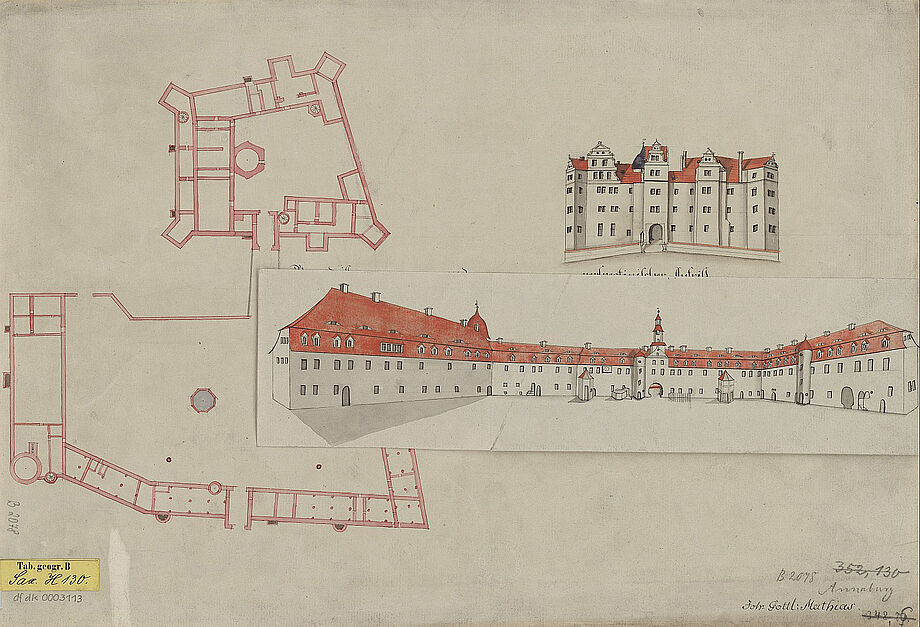
- In 1574, Elector August I had his book collection moved to Annaburg near Torgau, where it remained until his death (1586).
- The first catalogue of the electoral "Liberey" dates from the same year.
- In 1586, the "Liberey" was brought back to the palace in Dresden on the orders of Elector Christian I after the death of his father.
Götze, Johann Christian: Die Merckwürdigkeiten der Königlichen Bibliotheck zu Dreßden : Ausführlich beschrieben, und mit Anmerckungen erläutert. - Dresden : Walther, 1743-1748
Ebert, Friedrich Adolf: Geschichte und Beschreibung der königlichen öffentlichen Bibliothek zu Dresden. - Leipzig : Brockhaus, 1822
Falkenstein, Constantin Karl: Beschreibung der königlichen öffentlichen Bibliothek zu Dresden. - Dresden : Walther, 1839
Sächsische Landesbibliothek Dresden 1556-1956 : Festschrift zum 400-jährigen Bestehen. - Hrsg. von Karl Assmann ... - Leipzig: Harrassowitz, 1956
Handbuch der historischen Buchbestände in Deutschland / hrsg. von Bernhard Fabian. - Bd. 17 (Sachsen, A - K) / hrsg. von Friedhilde Krause. Bearb. von Waltraut Guth und Dietmar Debes. - Hildesheim : Olms-Weidmann, 1997, S. 96-102.
Das ABC der SLUB : Lexikon der Sächsischen Landesbibliothek - Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek Dresden. - Hrsg. von Thomas Bürger und Konstantin Hermann. - Dresden : Michel Sandstein Verlag, 2006. - (Schriftenreihe der Sächsischen Landesbibliothek - Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek ; 11)